FIA
La Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile, commonly referred to as the FIA, is a non-profit association established as the Association Internationale des Automobile Clubs Reconnus (AIACR) on June 20. 1904, 46 years before the first championship F1 race was held and around the time that the world's first motor races were taking place. Given that road cars had only gone into production at the end of the 1800s there was a need for an organisation to govern not only motorsport but also the emerging motoring industry and hence the FIA was born, to represent the interests of motoring organizations and motor car users.
To the general public, the FIA is mostly known as the governing body for motor racing events.
Headquartered at 8, Place de la Concorde, Paris, the FIA consists of 213 national member organizations in 125 countries worldwide.
As is the case with football's FIFA, the FIA is generally known by its French name and acronym, even in English -speaking countries, but is occasionally rendered as International Automobile Federation.
In 1922, the FIA delegated the organization of automobile racing to the Commission Sportive Internationale (CSI), an autonomous committee that later became the Fédération Internationale du Sport Automobile (FISA). A restructuring of the FIA in 1993 led to the disappearance of the FISA, putting motor racing under direct management of the FIA. Today FIA federation represents 227 national motorsport and motoring organisations from 132 countries including the world's biggest group, the American Automobile Association (AAA). This alone has over 50m members and, in total, FIA clubs represent well over 100.000.000 motorists and their families.
Trough the years federation has used its position and power to wield considerable influence on consumers and car manufacturers alike by developing initiatives such as the Euro NCAP rating system which has become the de facto standard for judging the safety of road cars.
In a sporting sense, the FIA operates like other governing bodies. In every country where it operates it has a member which holds the national sporting power necessary to sanction motor races. It also works with marshals and stewards at the events to ensure standards are maintained.
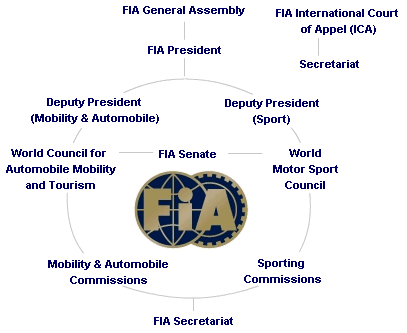
Any general problems of FIA policy are dealt with by its senate which comprises a team of 10 members drawn from the federation's clubs and management. They include Todt and Mosley as well as Nick Craw who is the senate's president and is also chief executive of ACCUS, the sporting counterpart to AAA, which sanctions all motor racing in the US. Sporting matters are resolved by the World Motor Sport Council, a 26-man board who all come from within the sport and are presided over by Todt. The external experts who handle disputes at the FIA work for its International Court of Appeal (ICA) which hears challenges to World Council decisions.
All the FIA members normally meet once a year at a General Assembly and the cost for entertaining hundreds of members comes to around $150,000. Decisions are made there on overarching matters for motorsport or the federation such as approving the F1 calendar. Since the FIA is a non-profit making organisation it needs to show a revenue for every cost but it doesn't need to file accounts.
However, F1's industry monitor Formula Money estimates that for a sport which has billions of dollars poured into it, the FIA gets by on relatively modest revenues.
The FIA has two branches - FIA France and FIA Switzerland with the former receiving revenues from sporting activities and the latter carrying the majority of the federation's personnel costs. According to Formula Money, the FIA's total operating income comes to around $65m with expenses matching this. One of its biggest costs is the combined total of approximately $25m spent on personnel, travel and entertainment. Surprisingly this doesn't even include a salary for Todt since his is an unpaid position. The FIA's revenue generally comes from member club subscriptions, registration and entry fees for racing series and annual fees from motorsport commercial rights holders. F1 provides a trifling amount of this.
The commercial rights to F1 only bring the FIA around $10m annually due to a deal Mosley did with F1's boss Bernie Ecclestone in 1995. The rights are ultimately owned by the FIA but prior to 1995 the federation handed them to the teams and received a 30% share. Ecclestone negotiated the sale of the rights on behalf of the teams but the deal done with the FIA saw the rights handed directly to his company Formula One Management (FOM) until 2010. F1 also brings around $5.5m to the FIA from registration and entry fees as well as the cost of drivers' super licenses. This put the FIA's total take from the sport at around $15.5m. In contrast, the commercial rights fees and registration income from World Rally as well as all other series, such as GT3 and World Touring Car, came to around $22.5m.
The FIA's decisions aren't always liked by F1's participants and the media but that is inevitable given its position of power over many competing interests. The irony is that while the FIA's ultimate power is perhaps its biggest strength it also makes it an easy target for criticism.
The FIA General Assembly is The Federation's supreme governing body, consisting of the presidents of the FIA's numerous member clubs.
The head of the FIA and chairman of the General Assembly is the President. The President is elected to a four-year term by the FIA General Assembly, and from October 2005 onward is not permitted to serve more than two terms. The current President, who took office in 2009 and began his first term is Jean Todt
To learn more about Formula 1 autorities and low makers check my article about administrative forces.
2.1 Role of the FIA :
The following technical regulations for Formula One cars are issued by the FIA.
The FIA will organise the FIA Formula One World Championship (the Championship) which is the property of the FIA and comprises two titles of World Champion, one for drivers and one for constructors. It consists of the Formula One Grand Prix races which are included in the Formula One calendar and in respect of which the ASNs
and organizers have signed the organization agreement set out in Appendix 4.
All the participating parties (FIA, ASNs, organizers, competitors and circuits) undertake to apply as well as observe the rules governing the Championship and must hold FIA Super Licences which are issued to drivers, competitors, officials, organisers and circuits.2.2 The Championship and each of its Events is governed by the FIA in accordance with the Regulations.
Event means any event entered into the FIA Formula One Championship Calendar for any year commencing at the scheduled time for scrutineering and sporting checks and including all practice and the race itself and ending at the later of the time for the lodging of a protest under the terms of the Code and the time when a technical or sporting certification has been carried out under the terms of the Code.4) LICENCES
4.1 All drivers, competitors and officials participating in the Championship must hold a FIA Super Licence.
Applications for Super Licences must be made annually to the FIA through the applicant's ASN.
Back to the top of the page







